What is the Biggest Risk Factor for Mesothelioma?
Introduction
Mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer primarily caused by exposure to asbestos. Understanding the biggest risk factor for mesothelioma is crucial for prevention, early diagnosis, and effective treatment. This article delves into the primary risk factor—asbestos exposure—along with other contributing factors, demographics, and preventive measures.
Understanding Mesothelioma
What is Mesothelioma?
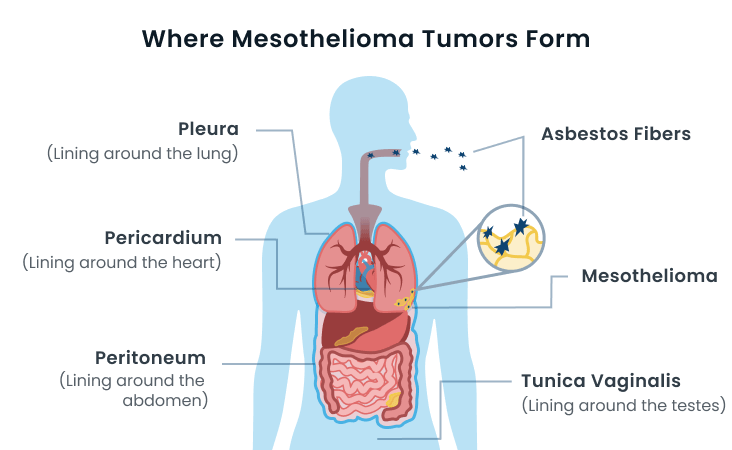
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a protective lining that covers many internal organs. The most common form is pleural mesothelioma, which affects the lining of the lungs. Other types include peritoneal mesothelioma (affecting the abdominal lining), pericardial mesothelioma (affecting the heart lining), and testicular mesothelioma.
Causes of Mesothelioma
The primary cause of mesothelioma is asbestos exposure. Asbestos fibers can become lodged in the lungs or other organs, leading to inflammation and cellular damage over time. The latency period for mesothelioma can be long, often taking 20 to 60 years after exposure for symptoms to manifest.
Symptoms of Mesothelioma
Symptoms may vary based on the type of mesothelioma but can include:
- Pleural Mesothelioma: Chest pain, persistent cough, shortness of breath, weight loss.
- Peritoneal Mesothelioma: Abdominal pain, swelling, nausea, unexplained weight loss.
- Pericardial Mesothelioma: Chest pain, difficulty breathing.
- Testicular Mesothelioma: Swelling or mass in the testicle.
The Biggest Risk Factor: Asbestos Exposure
Overview of Asbestos
Asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral that was widely used in construction materials, insulation, and various industrial applications due to its fire-resistant properties. It was commonly found in materials such as insulation, floor tiles, roofing, and drywall. However, when asbestos fibers are inhaled or ingested, they can lead to serious health issues.
How Asbestos Causes Mesothelioma
When asbestos fibers are inhaled or ingested, they can become lodged in the mesothelial cells lining the lungs or abdomen. Over time, these fibers cause irritation and inflammation, leading to genetic mutations that can result in cancerous growths. The risk of developing mesothelioma increases with the duration and intensity of exposure.
Statistics on Asbestos Exposure
According to research:
- More than 80% of mesothelioma cases occur in people with a confirmed history of asbestos exposure.
- Approximately 3,000 new cases of mesothelioma are diagnosed each year in the United States alone.
Occupational Exposure
Occupational exposure remains the most significant risk factor for developing mesothelioma. Certain professions are more likely to involve asbestos exposure:
| Occupation | Risk Level Description |
|---|---|
| Construction Workers | Often work with asbestos-containing materials like insulation. |
| Shipyard Workers | Exposure during shipbuilding and repair activities. |
| Firefighters | Risk from older buildings containing asbestos during firefighting efforts. |
| Power Plant Workers | Asbestos found in old pipes and insulation materials. |
| Veterans | Military personnel exposed to asbestos in ships and barracks. |
| Demolition Workers | Risk from tearing down buildings containing asbestos materials. |
| Mechanics and Machinists | Exposure from working with brake linings and other materials containing asbestos. |
Other Contributing Risk Factors
While asbestos exposure is the primary cause of mesothelioma, several other factors can increase an individual’s risk:
- Age: Most diagnoses occur in individuals aged 65 and older due to the long latency period associated with asbestos exposure.
- Gender: Men are disproportionately affected by mesothelioma compared to women because they are more likely to have worked in industries with high asbestos use.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations (e.g., BAP1 gene mutation) can increase susceptibility to developing mesothelioma.
- Environmental Exposure: Living near industrial sites where asbestos was used or disposed of can increase risk.
- Secondary Exposure: Family members of workers exposed to asbestos may inhale fibers carried on clothing or skin.
Age as a Risk Factor
Age is a significant factor in the likelihood of developing mesothelioma:
- Most diagnoses occur in individuals aged 65 and older.
- Approximately 64% of mesothelioma cases occur in patients aged 55 and older.
Gender Disparities
Men are more likely than women to develop mesothelioma due to historical occupational exposure patterns:
- Men are more likely to have worked in industries with high asbestos use.
- Women often experience secondary exposure through family members who worked with asbestos.
Genetic Predispositions
Certain genetic factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing mesothelioma:
- BAP1 Gene Mutation: Individuals with mutations in this gene may have a higher risk of developing mesothelioma at an earlier age.
- Family history of mesothelioma can also elevate risk levels.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can contribute to asbestos exposure:
- Living near industrial sites where asbestos was used or disposed of can increase risk.
- Natural deposits of asbestos can release fibers into the air during mining or construction activities.
Secondary Exposure Risks
Secondary exposure occurs when individuals come into contact with asbestos fibers brought home by someone who has been directly exposed:
- Family members of workers exposed to asbestos may inhale fibers carried on clothing or skin.
- This type of exposure has been documented in many cases where spouses or children develop mesothelioma.
Prevention Strategies
While it may not be possible to eliminate all risks associated with mesothelioma, certain strategies can help reduce exposure:
- Occupational Safety Measures: Implementing strict safety protocols in industries where asbestos is present can minimize exposure risks.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Education about the dangers of asbestos can help individuals avoid unnecessary exposure.
- Regular Health Screenings: Early detection through regular health check-ups can lead to better outcomes for those at higher risk.
Conclusion
Understanding the biggest risk factor for mesothelioma—asbestos exposure—is essential for prevention and early intervention strategies. Occupational exposure remains the primary risk factor, particularly among older men who have worked in industries known for using asbestos. Genetic predispositions and environmental factors also play a role in increasing risk levels.By raising awareness about these risks and implementing preventive measures, we can work towards reducing the incidence of this devastating disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the biggest risk factor for developing mesothelioma?
The biggest risk factor for developing mesothelioma is asbestos exposure, particularly occupational exposure over extended periods.
Are there other factors that contribute to the risk?
Yes, age, gender, genetic predispositions (such as BAP1 mutations), environmental exposures, and secondary exposures also contribute to increased risk levels.
How does age affect the likelihood of getting mesothelioma?
Most diagnoses occur in individuals aged 65 and older due to the long latency period associated with asbestos-related diseases.
Why are men more likely than women to develop mesothelioma?
Men are more likely than women to have worked in industries with high levels of asbestos use historically.
Can genetic factors influence my risk?
Yes, certain genetic mutations like those affecting the BAP1 gene can increase susceptibility to developing mesothelioma.
How can I reduce my risk?
Reducing occupational and environmental exposures to asbestos is crucial for minimizing your risk of developing mesothelioma.
Table: Summary of Risk Factors for Mesothelioma
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Asbestos Exposure | Primary cause; especially occupational exposure |
| Age | Higher incidence among those aged 65+ |
| Gender | Men are more likely than women |
| Genetic Factors | BAP1 mutations increase susceptibility |
| Environmental Exposure | Living near industrial sites |
| Secondary Exposure | Contact with fibers brought home by workers |
For additional information on mesothelioma and its associated risks, you can refer to Wikipedia on Mesothelioma.